책문제풀기 - 3
2021. 11. 9. 20:44ㆍ코딩/C언어
1.401P
include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int stock[25][200];
double sight[50][2];
char word[15000][46];
return 0;
}
2.402P
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char mark[5][5] = { 0 };
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if (i == j) printf("%c",mark[i][j] = 'x');
else printf(" ");
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}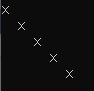
2.402-2P
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char mark[5][5] = { 0 };
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if ((i == j) || (i==4-j)) printf("%c", mark[i][j] = 'x');
else printf(" ");
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
3.412P
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char *pa[5] = { "apple", "pear", "peach", "banana", "melon" };
}3.412-2P
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a[4][10] = { "horse","fox","hippo","tiger" };
char* pa[] = { a[0],a[1], a[2], a[3] };
int count;
int i;
count = sizeof(pa) / sizeof(pa[0]);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("%c", pa[i][i]);
}
return 0;
}
4.413P
답 pary[4] = "orange";
pary는 배열요소가 4개이므로 0~3까지의 첨자만 들어갈수 있다.
5.425P
#include <stdio.h>
void print_str(char** pps, int cnt);
void sort_str(char** pps, int cnt);
int main(void)
{
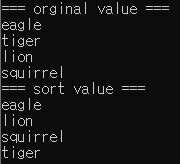
char* ptr_ary[] = { "eagle", "tiger", "lion", "squirrel" }; // 초기화
int count; // 배열 요소 수를 저장할 변수
count = sizeof(ptr_ary) / sizeof(ptr_ary[0]); // 배열 요소의 수 계산
printf("=== orginal value ===\n");
print_str(ptr_ary, count); // 배열명과 배열 요소 수를 주고 호출
printf("=== sort value ===\n");
sort_str(ptr_ary, count); // 배열명과 배열 요소 수를 주고 호출
print_str(ptr_ary, count); // 배열명과 배열 요소 수를 주고 호출
return 0;
}
void print_str(char** pps, int cnt) // 매개변수로 이중 포인터 사용
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < cnt; i++) // 배열 요소 수만큼 반복
{
printf("%s\n", pps[i]); // 이중 포인터를 배열명처럼 사용
}
}
void sort_str(char** pps, int cnt) // 매개변수로 이중 포인터 사용
{
char* temp;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < 4; j++)
{
if (*(pps[i]) > *(pps[j]))
{
temp = pps[i];
pps[i] = pps[j];
pps[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
6.436P
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
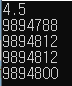
double grade = 4.5;
double* pg = &grade;
double** ppg = &pg;
printf("%.1lf\n", **ppg);
printf("%u\n", &ppg);
printf("%u\n", *&pg);
printf("%u\n", *ppg);
printf("%u\n", &*ppg);
}
7.437P
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
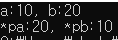
int a = 10, b = 20;
int* pa = &a, * pb = &b;
int** ppa = &pa, ** ppb = &pb;
int* pt;
pt = *ppa;
*ppa = *ppb;
*ppb = pt;
printf("a:%d, b:%d\n", a, b);
printf("*pa:%d, *pb:%d", *pa, *pb);
return 0;
}
8.497P
#include <stdio.h>
struct address
{
char name[20];
int age;
char tel[20];
char addr[80];
};
void print_list(struct address* lp);
int main(void)
{
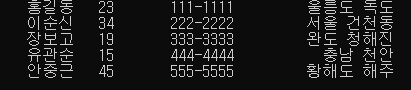
struct address list[5] = {
{"홍길동", 23, "111-1111","울릉도 독도"},
{"이순신", 34, "222-2222","서울 건천동"},
{"장보고", 19, "333-3333","완도 청해진"},
{"유관순", 15, "444-4444","충남 천안"},
{"안중근", 45, "555-5555","황해도 해주"}
};
print_list(list);
return 0;
}
void print_list(struct address* lp)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%10s%5d%15s%20s\n",
(lp + i)->name, (lp + i)->age, (lp + i)->tel, (lp + i)->addr);
}
}
'코딩 > C언어' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] Circulr Queue / Sort(bubble, selection) (0) | 2021.11.09 |
|---|---|
| 책문제풀기 - 2 (0) | 2021.11.09 |
| 책문제 풀기 - 1 (0) | 2021.11.09 |